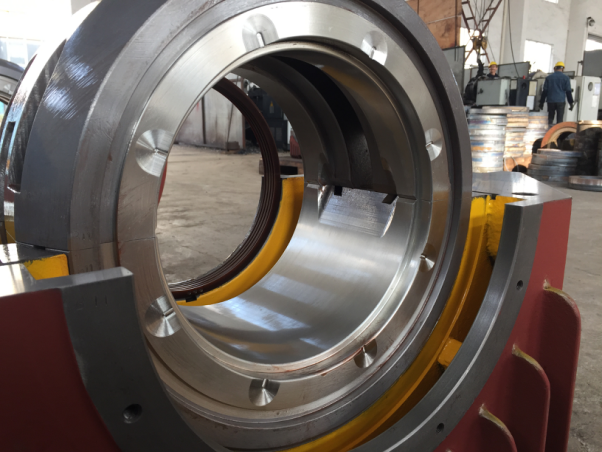
With the development of market economy and the implementation of national energy policies, equipment in industries such as mining, cement, steel, and electric power are developing towards large-scale, and the demand for large motors is also increasing. Large motor bearings are mostly split radial sliding bearings, mainly made of babbitt alloy. During assembly, scraping and grinding methods are generally used to meet the accuracy requirements and ensure its performance. Therefore, the quality of grinding is crucial to the normal operation of the motor, and directly affects the service life of the motor. The scraping and grinding quality is poor, and it is easy to cause the bearing bush to develop from partial adhesion damage to most adhesion damage in a very short period of time during the motor test run, until the bearing bush cannot be used due to shaft burning. Therefore, when scraping and grinding the bearing shells, they are all operated by experienced bench workers.
The following describes the scraping method of split sliding bearings (bearing shells).
1. Matching requirements for bearing shells, bearing seats, and bearing caps
(1) The contact area between the back of the lower bearing pad and the bearing seat should be greater than 70%, and the distribution should be uniform. The contact range angle should be greater than 150 °, and the clearance of the remaining parts with clearance allowed should not be greater than 0.05 mm.
(2) The contact area between the back of the upper bearing shell and the bearing cover should be greater than 60%, and the distribution should be uniform. The contact range angle should be greater than 120 °, and the gap between the parts with gaps allowed should not be greater than 0.05 mm.
2. Technical requirements for scraping and grinding of bearing pads
2.1 Contact angle and contact spot requirements
The contact angle of the bearing bush is within the range of 60 °~120 °, with the small value selected for light load and the large value selected for heavy load; Generally, within a 60 ° (or 120 °) arc, there should be more than two lower bearing pads and more than one upper bearing pad with evenly distributed contact points per square centimeter of area.
2.2 Oil groove and bearing oil groove belt
(1) In split sliding bearings, the oil groove is generally opened on the upper bearing with less stress. The cross section is a semicircular arc, distributed 180 ° along the inner circumference of the upper tile, and is machined. Due to the existence of a gap in the upper bearing, lubricating oil can easily enter between the upper bearing surface and the shaft, and its main function is to smoothly inject lubricating oil into the inner (radial) oil groove of the bearing.
(2) The oil groove belt at the bearing mouth is distributed at the joint of the upper and lower bearing shells (both sides). The oil groove belt is in an arc wedge shape, with a depth of 1 mm to 3 mm from the outer side of the joint surface of the bearing opening. The width of the oil groove belt is generally 8 mm to 40 mm. The size of the single side of the oil groove belt from the bearing end surface is generally 8 mm to 25 mm. The length of the oil groove belt is about 85% of the axial length of the bearing pad. It is a strip oil groove that can store a large amount of lubricating oil, facilitating lubrication and cooling of the bearing pad and shaft.
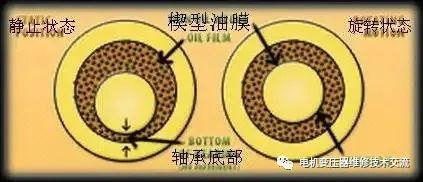
2.3 Lubricating oil wedge
The lubricating oil wedge is located at the connection between the oil groove belt and the bearing bush within the contact angle and is formed by manual scraping (commonly known as the scraping mouth). Its main function is to store oil to cool the bearing shells and shafts; The second is to use its circular wedge angle to continuously suck lubricating oil into the bearing part under the drive of shaft rotation, forming an oil film to fully lubricate the bearing bush and shaft. The lubricating oil wedge is a circular arc wedge angle composed of two irregular circular arcs, which smoothly connects the oil groove belt and the working contact surface of the bearing pad. The scraping and grinding of the lubricating oil wedge should be carried out when the fine scraping of the bearing bush is basically completed, and it is not advisable to scrape and grind in advance.
2.4 Top clearance and side clearance of bearing shells
(1) When there are no special requirements, the top clearance of the bearing pad can be taken as 1 ‰ to 2 ‰ of the shaft diameter based on experience, and should be selected within this range based on rotational speed, load, and lubricating oil viscosity.
(2) The side clearance of the bearing bush shall be 1/2 of the top clearance when there are no special requirements; For smaller tip gaps, each side gap is equal to the tip gap. The side clearance of the bearing bush is manually scraped as required. The side clearance extends from the joint surface of the bush mouth to the specified working contact angle area, and is axially connected to the oil groove belt and lubrication wedge angle. This part should not be in contact with the shaft, and attention should be paid to this point during scraping. The sharp corner between the side gap and the pad opening plane should be chamfered, which is generally 1 depending on the size of the bearing pad × 45°~3 × 45°.
3. Scraping and lapping process of split bearing shells
3.1 Scraping and grinding of tile back
The contact condition of the upper and lower bearing pads should be checked using the coloring method and coated with red lead powder based on the tile base and tile cover, and the tile back should be trimmed with a fine file until the requirements are met.
3.2 Rough scraping of bearing shells
(1) Slightly scrape the machining tool marks on the upper and lower bearing shells. It is required that the surface of the bearing shells be completely scraped, and the scraping and grinding shall be uniform to remove the machining marks.
(2) Apply a thin layer of display agent (red lead powder or other) to the shaft neck, and rough scrape the upper and lower bearing pads several times. After the contact area and grinding points are evenly distributed, turn to fine scraping. During rough scraping, it should be noted that the part of the tile mouth cannot be scratched out, and full contact within a 180 ° range is required.
3.3 Fine scraping of bearing shells
When fine scraping the bearing pads, the upper and lower bearing pads should be padded (the joint surface of the pad mouth). After assembly, scrape and grind the bearing pads at both ends, coat the pads with red lead powder, and grind the points with the shaft. When starting the pressing assembly, the pressing force should be uniform, and the shaft should not be pressed too tightly. It can only be rotated as soon as it is scraped, cushioned, and pressed. At this time, it should also be noted not to scrape the bearing mouth out. After multiple scrapes and grinding, the contact surface spots of the bearing pad can be densely and evenly distributed.
3.4 Fine scraping of bearing shells
The purpose of fine scraping is to scrape and grind the contact spot and contact area to the specified technical requirements. At this time, without using the display agent, slightly add a bit of turbine oil. The polishing method is the same as that of fine scraping, with the points varying from large to small, from deep to shallow, and from sparse to dense. During the polishing process, large points can be broken up with a scraper to become dense small points. After repeated polishing, gradually scraping until the requirements are met. When the fine scraping is about to end?, It is very important to scrape out the side clearance of the lubricating oil wedge (bearing opening) to achieve the service performance of the bearing bush.
More about Epen E90 Bushing:
E90 bronze wrapped bushings are made of entirely bronze CuSn8. Because of material properties, the working surface rolled with diamond Indentations (standard Indentations) or stamped oil grooves according to detailed application. And it also has good performance of anti-corrosion caused by chemical and environments. During the operation, the grease & oil will be released from the indentations, which allow for long-term lubrication. Compare with machined bronze bearings, E90 can offer some advantages including thin wall, lower weight, cheaper cost, high load etc. It is suitable for high load, lower speed application like construction, transport, and agriculture machinery.
http://www.cnepen.com/showinfo-216-559-0.html